How to Read a Token Model
A Real Example of an Investment Made
The blockchain space is currently engaged in a heated debate over the best token model to adopt. With many options available, selecting the best approach can be challenging, especially given the fast-paced nature of this market. Models range from deflationary examples like Bitcoin to inflationary ones like Tezos, and each project has its unique way of managing contributions and incentives.
One of the most critical factors for a token's survival is determining the appropriate total supply while allowing sufficient time and space for the ecosystem to grow. Decisions concerning the token during the Token Generation Event (TGE), the timing of vesting periods, emission rates, and listing prices can make all the difference to a project’s future sustainability.
Investors and traders can also benefit from the transparency offered by blockchain technology. There are many online tools out there like Token Unlocks, that allow precise tracking of token unlocking schedules, enabling traders to seize profitable opportunities.
In this article, we will explore the key distinctions between narrow versions of inflationary and deflationary models. Additionally, we will delve into broader considerations that encompass vesting and token unlocking policies, supported by real-life examples of tokens trading in the market. We will also share insights on how to leverage these opportunities from a trading perspective, providing a battle-tested and effective trading strategy. After reading this article, you'll gain valuable knowledge to guide your decisions on token economics models.
Policies on Total Supply
In the context of blockchain-based assets, broadly, tokens with inflationary and deflationary models refer to how the total supply of the tokens changes over time. These models impact the token's scarcity, purchasing power, and overall economic dynamics. Let's explore the differences between the two main models:
Inflationary Model
In an inflationary model, the total supply of tokens increases over time. This means that new tokens are continuously minted or created, leading to an ever larger supply. The rate of token creation is often governed by a predetermined monetary policy encoded in the blockchain protocol.
The inflationary model is usually adopted to incentivize certain behaviors, such as securing the network (e.g., through Proof of Stake) or encouraging participation in governance. In theory, an inflationary model can lead to a decrease in the token's purchasing power over time since the supply increases, which could result in a gradual decrease in the token's value.
Some cryptocurrencies like Cardano (ADA) or Tezos (XTZ) have implemented inflationary models to reward stakeholders who participate in network operations or voting.
Benefits
Incentives: An inflationary model can incentivize various behaviors that benefit the network or ecosystem. For example, it encourages stakeholders to participate in staking (if the consensus mechanism is Proof of Stake), voting, or providing resources to maintain network security.
Reward for Adoption: Inflation can reward early adopters who actively participate in the network's development and growth. This can attract more users to the ecosystem, fostering a larger and more engaged community.
Funding Mechanism: Inflation can serve as a funding mechanism for ongoing development, research, and maintenance of the network. Projects can allocate a portion of the newly minted tokens to fund these activities.
Drawbacks
Purchasing Power Erosion: Over time, the continuous issuance of new tokens can lead to a decrease in the token's purchasing power. As the supply increases, the value of each individual token may decrease, potentially leading to inflationary pressure.
Inflationary Spirals: If the inflation rate is not carefully managed, it can lead to inflationary spirals, where the value of the token decreases rapidly, eroding user confidence and hampering adoption.
Misaligned Incentives: Inflationary models might cause divisions between different stakeholders, as there is usually a class that has an advantage over the other and is less hurt by the brunt force of inflation.
This model is very similar to the Fractional Reserve Banking model in operation today in the traditional financial system. Commercial banks are allowed to lend out a portion of the deposits they receive, while keeping only a fraction of those deposits in reserve. This effectively creates new money in the economy, leading to an increase in the money supply.
Deflationary Model
In a deflationary model, the total supply of tokens is fixed or decreases over time. This can be achieved through various mechanisms, such as token burning (destroying tokens), fixed supply with no new token issuance, or mechanisms that remove tokens from circulation based on certain events.
The deflationary model is often intended to create scarcity and potentially increase the value of the token over time, as the available supply reduces. In theory, a deflationary model can lead to an increase in the token's purchasing power over time since the supply decreases, which could result in a gradual increase in the token's value.
The most well-known example of a deflationary model is Bitcoin (BTC), which has a fixed supply cap of 21 million coins. As new coins are mined, the rate of supply growth decreases over time, eventually leading to a capped and finite supply.
Benefits
Scarcity and Increased Value: The limited or decreasing supply of tokens can create scarcity, leading to increased demand and potentially driving up the token's value over time.
Incentive for Long Term Holding: A deflationary model can incentivize long term holding, as those who acquire tokens early on may benefit from their increased value as the supply decreases.
Protection against Inflation: Inflationary models, such as those seen in traditional fiat currencies, can lead to a loss of purchasing power over time. A deflationary model, on the other hand, can serve as a hedge against inflationary pressures.
Drawbacks
Potential Hoarding: While users may have an incentive to hold on to tokens due to their potential appreciation, excessive hoarding could hinder the token's use as a medium of exchange in day-to-day transactions.
Lack of Incentives for Network Participation: In some cases, deflationary models may not provide sufficient incentives for users to actively participate in network maintenance or governance, as token scarcity might discourage spending.
Lack of Funding Mechanism: Deflationary assets are scarce, and could run into the problem towards the end of the emission cycle of not having enough resources to finance the growth of the network.
This model is more akin to the Gold Standard that was prevalent in the 19th and 20th century where the paper currency was tied to a certain supply of gold held in the coffers of the central banks around the world.
The ongoing debate about token models in the blockchain space is reminiscent of the question that kickstarted the entire blockchain movement - the issue of having an infinite money printer. This was precisely what Bitcoin aimed to address: the idea of an inflationary model with unlimited printing replicates the same problem we see in traditional markets. This is the main reason why people are actually fleeing these markets to switch to crypto.
While these inflationary models may start with good intentions, over time, the human factors of greed often lead to alterations in economic incentives. It becomes political. This can result in some individuals manipulating the system by printing more currency and diverting it for their own gain. On the other hand, deflationary systems, with their limited token supply, and especially if monetary policy is managed by a machine, keep all participants in check and prevent them from experiencing price deflation due to misguided monetary policies.
The lessons learnt in the past 100 years shouldn’t be forgotten.
Do you want a deeper dive on these concepts ? Book a free call with one of our experts. We’ll help you understand and apply this knowledge for yourself, your project or your portfolio.
Policies on Token Unlocks
Another important factor that is paramount for the success of any token and its price traction in the future is a correct design of the token economics and unlock policies. Some are clearly designed to reward institutional speculators - we’re not referring to retail traders here - and others have incentives that are aligned towards the development of the community over time.
If we take a look at over 65% of all tokens that have been launched on the market —read our past article outlining this research here: link — are currently over 90% below their TGE price. Certainly the general market drawdown has had a big impact, but if the token unlock schedule are also too aggressive…
What effects could this have on the price?
Very negative. A downward spiral can be formed where tokens held in the hands of retail investors are severely diluted by the aggressive unlocks from investors and team members. They monetize some of their assets by locking in the gain from their discounted purchase price at the expense of retail investors. If the unlocks happens during a market drawdown - as it did- there is even more pressure to sell if the coins locked are needed to cover other liabilities by stakeholders.
Many tokens don’t enjoy large volumes of trading, which means that each sale will impact the price disproportionately due to a lack of buyers. This further complicates the life of many companies and protocols that are already on the brink of implosion. There’s a vast number of zombies tokens walking around dead in the water.
It is important to talk about the difference between these aggressive token policies against a savvy construction of token unlocks that remain sustainable over the long term.
Some terminology:
Cliff: period of time elapsing in which the vesting is not active
Vesting: period over which the token unlocks are conducted
Example:
30% of total supply = 100,000
Cliff = 12 months
Vesting = 12 months
Starting from month 12, the tokens will unlock at 8,333 x month or 8.3% per month until reaching month 24.
Inflationary Vesting Schedules
An inflationary vesting schedule is a schedule of token unlocks that releases on the market large quantities of tokens over a relatively short time frame. Generally these tokens tend to have a large quantity unlocked already at TGE (> 20%) and an aggressive unlocking schedule with no cliff or under 12 months with vesting that is lower than 24 months. Another tell is that the treasury isn’t locked either and the team can flood the market with it at any whim.
As mentioned before, tokens with such inflationary vesting schedules generally tend to remunerate the team and investors disproportionately, while the brunt pain of dilution is mostly felt by retail buyers and smaller users of the tokens. It’s a game that a lot of venture capital investors have been playing.
If we draw a parallel with traditional finance, most crypto startups or ecosystems are still in their infancy, with maybe 2 or 3 years of development and they already list their token on the open market. This would be similar to a startup going public after three years from its inception. It would be very unusual. However, founders have been conditioned to list on CEXs and DEXs without thinking it through very much. It’s what everybody else does and so it’s easier to just follow along.
Venture Capitalists - the speculator ones at least - have seen this behavior as an opportunity. An opportunity to take advantage of an exit strategy that was never available to them before: a liquidity event as fast as 12 months against the usual 5 to 7 years. By participating in the private rounds, through SAFT agreements, they have often secured a 10-20x gain by only ensuring that the token gets listed, and through agreement with market makers, they can then dump the token on retail buyers. If they aren’t liquidating most of their tokens at the TGE, these investors generally structure their vesting timelines aggressively (< 24 months), allowing them to quickly sell off their stakes and thereby dilute the holdings of other token holders. They bolster marketing efforts during these periods to sustain momentum while they liquidate their positions.
Sometimes the team behind the projects are in on it, whereas most of the times they are just unaware of the implications of dilutionary pricing and vesting policies. Being able to forecast in advance how the vesting schedules and cash need will impact the business in 60 to 70 months is not an easy feat.
In crypto, oftentimes participants don’t seem to plan to wait for long and build something sustainable for the long term, but have otherwise opted for a quick cash grab. We’ve seen this scenario more times than we’d like to admit.
Non-Inflationary Vesting Schedule
A non-inflationary vesting schedule is one that releases the tokens over a long enough time horizon to ensure that there’s alignment between all stakeholders in the ecosystem.
The best cases are certainly Proof of Work blockchains and ecosystems. Apart from generally having a limited supply - i.e. deflationatory - they usually release tokens at a fixed and unchanging monetary policy that is dictated by algorithm and following the work produced by network participants.
The supply isn’t distributed through allocations and vesting schedules, but by the action that participants take in the network for a certain reward and an algorithm. The absence of the bias of the human element, and the lack of money in the hands of people that can’t have all sorts of incentives to pursue, these networks are governed by an unemotional algorithm and they can just participate in it.
Outside of PoW systems, we also have systems running on a Proof of Stake consensus that are more soundly designed even though they don't benefit from the intrinsic censorship resistance of PoW chains.
Prescriptions:
So, what principles should a sound token design follow ?
Let’s list a few:
The maximum supply should be established with a fixed cap and remain unalterable. During the initial token generation event (TGE), only a minor portion of tokens, less than 20%, should be introduced into circulation.
To ensure a structured approach, it is advisable to implement cliff periods of over 12 months for Teams, Advisors, and Investors, followed by aligned vesting periods spanning more than 60 months to encourage long-term commitment.
Applying a uniform policy, all allocations should be subjected to vesting periods, without exceptions. A strategic allocation of tokens should be earmarked to compensate ecosystem-related efforts, triggering supply inflation exclusively upon the completion of specific actions.
Furthermore, incorporating a burning mechanism into the system can gradually reduce the token supply over an extended period, establishing a deflationary stance that ensures sustainability over time.
We get it, these topics can feel complex. That's why we've rolled out our Token Policy Program. It's all about creating airtight token economics: from vesting to incentives, inflation models, KPIs, and ecosystem design.
With our assistance, you can sustainable token economy, sidestep pitfalls, and nail your protocol's goals.
Ready to dive in? Secure your free consultation here.
Case Study: BITDAO's Aggressive Coin Unlocking Policy
To clarify these concepts for you, let’s take a look at a concrete comparison between an inflationary token policy against a deflationary one.
BITDAO
Let’s take a look at $BIT’s token information:
$BIT
Total Supply: 10,000,000,000
Cliff (months): 3
Vesting (months):18
Unlock at TGE: 30%
Source: Token Unlocks
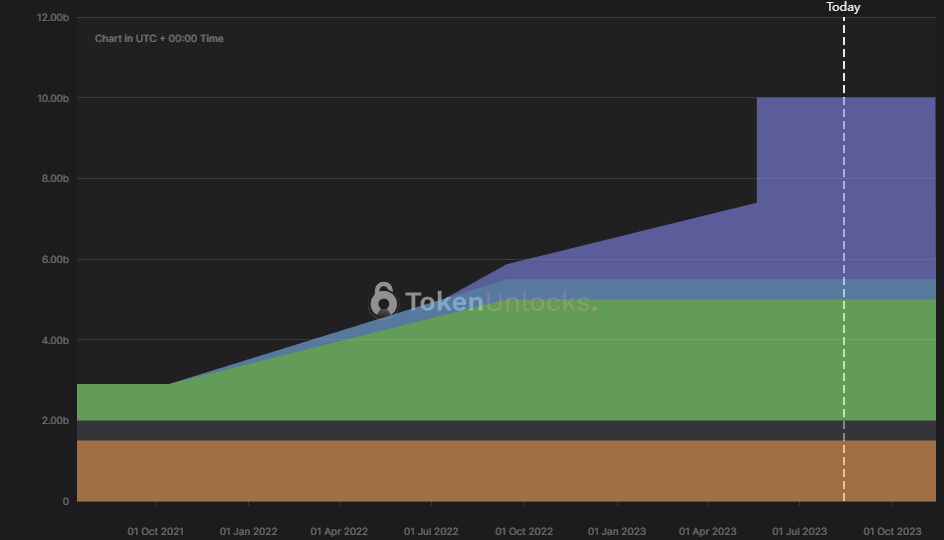
Below you can see a graph taken from Token Unlocks that showcases the vesting policies of BitDAO until the max supply is all in circulation:
Source: Token Unlocks
$BIT demonstrates a clear inflationary token economic policy, it’s evident from the graph. The duration between TGE and the complete circulation of all tokens amounts to just 18 months ! The TGE saw an influx of over 30% of the total supply into the market, with another substantial unlock of over 10% slated for May. For most of the locked tokens, there is a just 3-month cliff period.
The erosion of net worth for $BIT holders has been distressing, as the value of their investments has been quietly destroyed, and they probably didn’t even notice this sneaky effect. This depreciation could have been attributed to the bear market, without the realization that each $BIT was rapidly becoming less scarce.
How can we take advantage of this knowledge ?
Trading Idea
Let’s take a real life example by looking at a recent post made by our founder, @molto-social, on X.
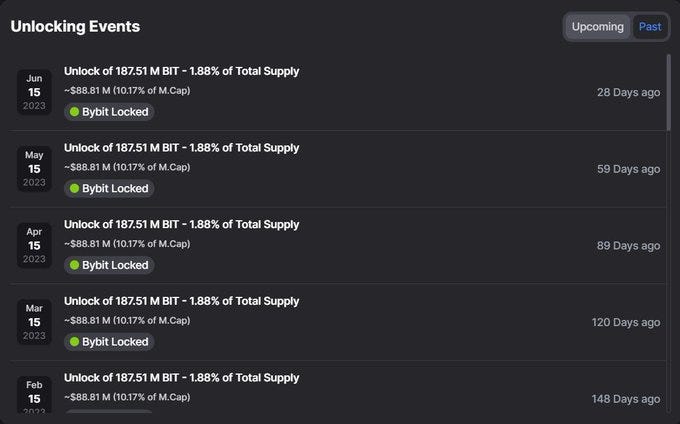
Our founder has examined BITDAO's monthly coin unlocking strategy, noticing they were about to release around 10% of the market cap on June the 15th. He then proceeded to illustrate both past and upcoming unlocks for $BITDAO.
Source: @molto-social
Such a large unlock, as we’ve stressed before, could put a lot of pressure on the price, especially around the unlocking dates.
To make the concept clearer, he then compared the performance of BITDAO against Bitcoin. As stated in the past, PoW blockchains tend to have a deflationary policy, as they have a fixed supply and the emission of new currency is governed by an unbiased algorithm and not by human intervention.
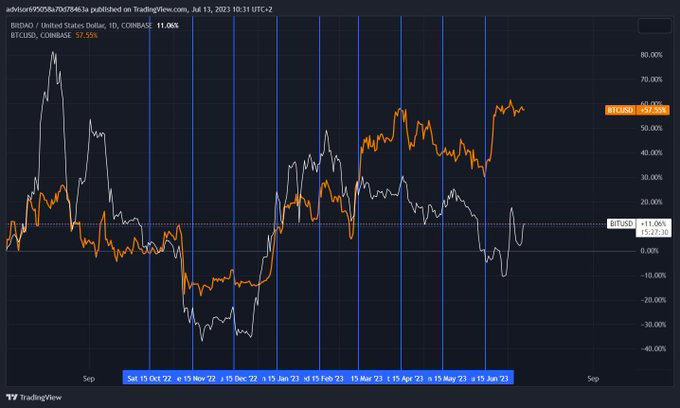
In the graph below, @molto-social visualizes for us the differential performance between the two assets. The graph clearly reveals how $BIT's value is influenced by its inflationary model, causing it to underperform compared to Bitcoin.
Source: @molto-social
The blue lines are BITDAO’s unlocks, the white graph represents the value of BITDAO, and the yellow graph illustrates the value of Bitcoin.
It is clearly visible how following the blue lines there has been downward pressure on BITDAO’s price and how on average, it has underperformed compared to Bitcoin.
How could we position ourselves to take advantage of this opportunity ?
Our founder has shared a simple trading tip you could take advantage of today:
Source: @molto-social
Taking advantage of the token unlocks, you could potentially position yourself on the short side as you know that large unlocks will most probably drive the price down as holders sell their tokens to obtain liquidity. This strategy is easy to deploy and it has a good probability of success.
Disclaimer:
None of the information reported in this report could be intended as investment advice or solicitation to buy any type of tokens or securities. The reader has complete control and responsibility over his decisions. Algo Capital and its employees and partners will never be liable for decisions taken by readers.
This is a simple go to strategy that any trader could take advantage of. But there are many more lessons that could be gleaned from the concepts outlined in this article.
For crypto entrepreneurs, the main lesson to grasp is that the token economic model plays a crucial role in the lasting success of their project. If your token's economic design prioritizes short-term gains for you and your investors at the expense of your users, it's unlikely to sustain long-term growth unless your intention is a quick rug-pull. To increase your project's chances of success, consider adopting a longer-term perspective, aligning incentives for all stakeholders, introduce a way to reduce your token supply while minimizing human decision-making which is prone to politics.
For investors, the key takeaway is to exercise caution and conduct thorough due diligence when evaluating the potential future impact of a project's token economic policy before making investment decisions. If your aim is a rapid buy and sell strategy, an inflationary token model might be more suitable, allowing for quicker token unlocking and selling before the price significantly drops. However, it's important to note that this approach leans more towards speculation than investment. On the other hand, if you have a long-term investment horizon, it's advisable to focus on projects where the underlying economic model supports the project's sustainability rather than seeking a quick exit. In either case, investors can benefit from strategic opportunities during token unlocks by either covering their positions to reduce losses or enhancing their returns through derivative strategies.
We hope this article was helpful in outlining the pro and cons of the different token economic models as well as equip you with actionable information that you can use for yourself or your business.
At Algo Capital, we've put in a lot of time and hard work in these areas, so you don't have to do the heavy lifting. Our team has spent thousands of hours studying, investing, and trading in these markets. Thanks to all this experience, we can help steer you toward the most battle-tested solutions.
No matter if you're a crypto founder trying to create or improve your token economic model or an investor looking to gain an hedge in these market, we can be your partner ensuring you succeed in the future.
To get started, just click the button below to set up a free call with us.